Group B Streptococcus Infections Caused by Improper Sourcing and Handling of Fish for Raw Consumption, Singapore, 2015–2016
Man L. Chau
1, Swaine L. Chen
1, Min Yap, Sri H.P. Hartantyo, Paul K.T. Chiew, Charlene J. Fernandez, Wai K. Wong, Rockey K. Fong, Wei L. Tan, Brian Z.Y. Tan, Youming Ng, Kyaw T. Aung, Kurosh S. Mehershahi, Christopher Goh, Joanne S.L. Kang, Timothy Barkham, Adeline O.K. Leong, Ramona A. Gutiérrez, and Lee C. Ng
Author affiliations: National Environment Agency, Singapore (M.L. Chau, M. Yap, S.H.P. Hartantyo, Y. Ng, K.T. Aung, C. Goh, J.S.L. Kang, A.O.K. Leong, R.A. Gutiérrez, L.C. Ng); Genome Institute of Singapore, Singapore (S.L. Chen); National University of Singapore, Singapore (S.L. Chen, K.S. Mehershahi); Agri-Food and Veterinary Authority of Singapore, Singapore (P.K.T. Chiew, C.J. Fernandez, W.K. Wong, R.K. Fong, W.L. Tan, B.Z.Y. Tan); Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (P.K.T. Chiew, L.C. Ng); Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore (T. Barkham)
Main Article
Figure 4
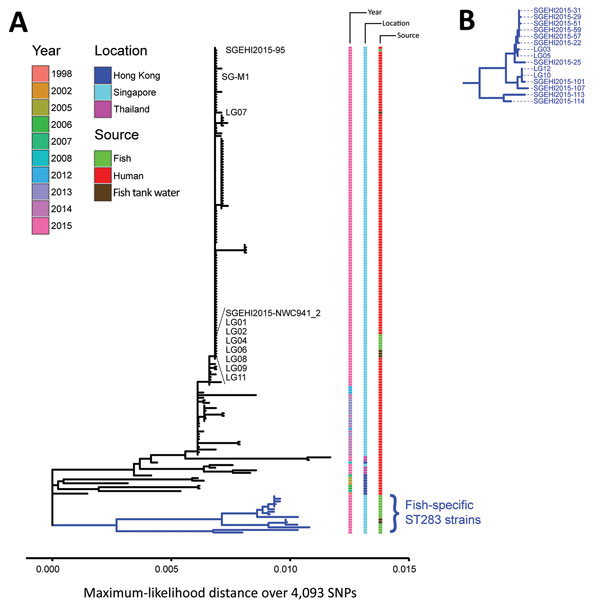
Figure 4. Phylogenetic analysis of group B Streptococcus (GBS) infections caused by improper sourcing and handling of raw fish for raw consumption, Singapore, 2015–2016. A) Maximum-likelihood single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)–based tree for GBS ST283 strains relative to the SG-M1 reference human outbreak strain. Year, location, and source (human or fish) for isolates are indicated. Twelve strains from 6 fish (SGEHI2015-NWC941, SGEHI2015–95, LG01, LG02, LG04, and LG06) and 4 fish tank water samples (LG07, LG08, LG09, and LG11) were nearly identical to the local reference outbreak strain SG-M1 (no SNP, 0 and 12 indels, respectively). Scale bar indicates distance over 4,093 total SNPs. B) Enlargement of blue subtree from bottom of tree in panel A showing fish GBS ST283 isolates that were different (57–71 SNPs and 11–33 indels) from the human outbreak strain. ST, sequence type.
Main Article
Page created: November 15, 2017
Page updated: November 15, 2017
Page reviewed: November 15, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
