Volume 29, Number 9—September 2023
Research
Genomic Characteristics of Emerging Intraerythrocytic Anaplasma capra and High Prevalence in Goats, China
Figure 4
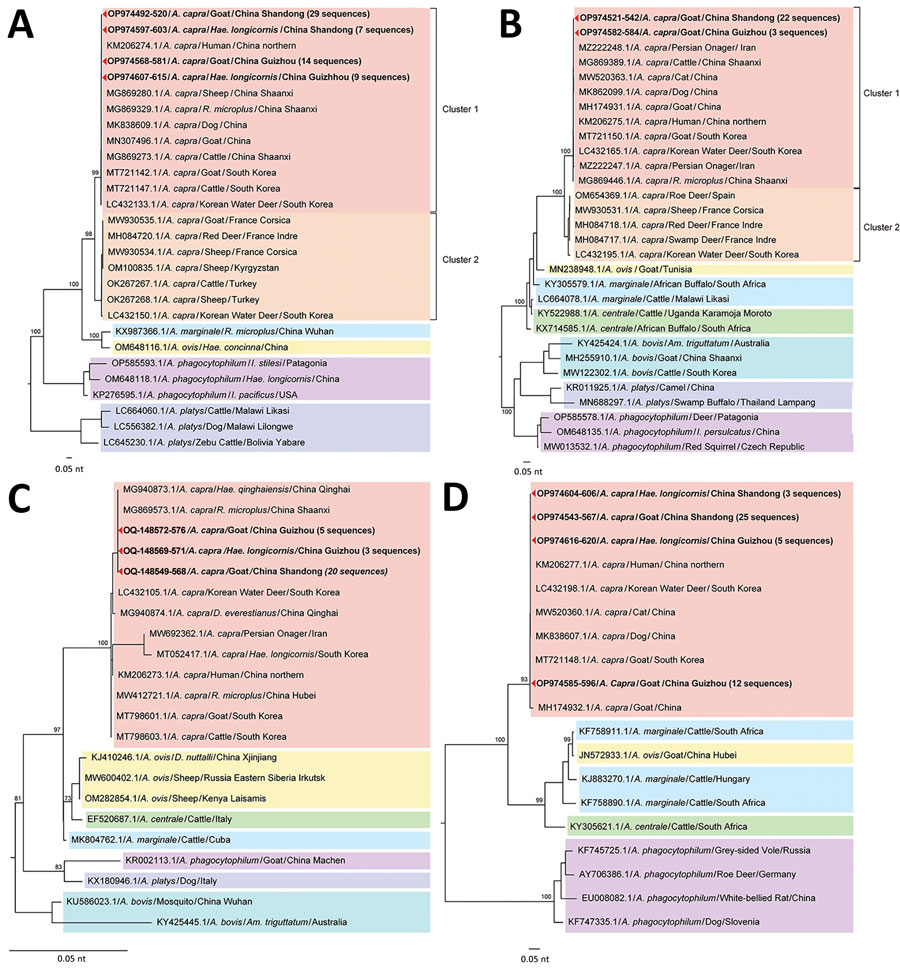
Figure 4. Phylogenetic analysis of Anaplasma capra based on nucleotide sequences of 4 genes in study of emerging intraerythrocytic A. capra and high prevalence in goats, China. A) Phylogenetic tree based on 536 bp nucleotide sequence of gltA. B) Phylogenetic tree based on 620 bp nucleotide sequence of groEL. C) Phylogenetic tree based on 860 bp nucleotide sequence of 16S rRNA. D) Phylogenetic tree based on 642 bp nucleotide sequence of msp4. We performed bootstrap analysis of 1,000 replicates to assess the reliability of the reconstructed phylogenies. GenBank accession numbers are provided. Scale bars show estimated evolutionary distance.
1These senior authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: July 08, 2023
Page updated: August 20, 2023
Page reviewed: August 20, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.