Loading AI tools
Astronomical treatise by Claudius Ptolemy From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Almagest (/ˈælmədʒɛst/ AL-mə-jest) is a 2nd-century mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Claudius Ptolemy (c. AD 100 – c. 170) in Koine Greek.[1] One of the most influential scientific texts in history, it canonized a geocentric model of the Universe that was accepted for more than 1,200 years from its origin in Hellenistic Alexandria, in the medieval Byzantine and Islamic worlds, and in Western Europe through the Middle Ages and early Renaissance until Copernicus. It is also a key source of information about ancient Greek astronomy.

Ptolemy set up a public inscription at Canopus, Egypt, in 147 or 148. N. T. Hamilton found that the version of Ptolemy's models set out in the Canopic Inscription was earlier than the version in the Almagest. Hence the Almagest could not have been completed before about 150, a quarter-century after Ptolemy began observing.[2][3]
The name comes from Arabic اَلْمَجِسْطِيّ al-majisṭī, with اَلـ al- meaning 'the' and majisṭī being a corruption of Greek μεγίστη megístē 'greatest'. The Arabic name was popularized by a Latin translation known as Almagestum made in the 12th century from an Arabic translation, which would endure until original Greek copies resurfaced in the 15th century.[citation needed]
The work was originally called Μαθηματικὴ Σύνταξις (Mathēmatikḕ Sýntaxis) in Koine Greek, and was also known as Syntaxis Mathematica in Latin. The treatise was later called Ἡ Μεγάλη Σύνταξις (Hē Megálē Sýntaxis), "The Great Treatise"; Latin: Magna Syntaxis), and the superlative form of this (Greek: μεγίστη megístē, 'greatest') lies behind the Arabic name from which the English name Almagest derives.

The Syntaxis Mathematica consists of thirteen sections, called books. As with many medieval manuscripts that were handcopied or, particularly, printed in the early years of printing, there were considerable differences between various editions of the same text, as the process of transcription was highly personal. An example illustrating how the Syntaxis was organized is given below; it is a Latin edition printed in 1515 at Venice by Petrus Lichtenstein.[4]
The cosmology of the Syntaxis includes five main points, each of which is the subject of a chapter in Book I. What follows is a close paraphrase of Ptolemy's own words from Toomer's translation.[7]

The layout of the catalogue has always been tabular.[9] Ptolemy writes explicitly that the coordinates are given as (ecliptical) "longitudes" and "latitudes", which are given in columns, so this has probably always been the case. It is significant that Ptolemy chooses the ecliptical coordinate system because of his knowledge of precession, which distinguishes him from all his predecessors. Hipparchus' celestial globe had an ecliptic drawn in, but the coordinates were equatorial.[10] Since Hipparchus' star catalogue has not survived in its original form, but was absorbed into the Almagest star catalogue (and heavily revised in the 265 years in between),[11][10] the Almagest star catalogue is the oldest one in which complete tables of coordinates and magnitudes have come down to us.
As mentioned, Ptolemy includes a star catalog containing 1022 stars. He says that he "observed as many stars as it was possible to perceive, even to the sixth magnitude". The ecliptic longitudes are given in terms of a zodiac sign and a number of degrees and fractions of a degree. The zodiac signs each represent exactly 30°, starting with Aries representing longitude 0° to 30°. The degrees are added to the lower limit of the 30-degree range to obtain the longitude. Unlike the situation with the zodiac of modern-day astrology, most of the stars of a given zodiac constellation in the catalog fall in the 30-degree range designated by the same name (the so-called 'zodiac sign'). The ecliptic longitudes are about 26° lower than those of AD 2000 (the J2000 epoch).[note 2] Ptolemy says that the ecliptic longitudes are for the beginning of the reign of Antoninus Pius (138 AD) and that he found that the longitudes had increased by 2° 40′ since the time of Hipparchus which was 265 years earlier (Alm. VII, 2). But calculations show that his ecliptic longitudes correspond more closely to around the middle of the first century CE (+48 to +58).[7][12][10]
Since Tycho Brahe found this offset, astronomers and historians investigated this problem and suggested several causes:

Subtracting the systematic error leaves other errors that cannot be explained by precession. Of these errors, about 18 to 20 are also found in Hipparchus' star catalogue (which can only be reconstructed incompletely).[15][10] From this it can be concluded that a subset of star coordinates in the Almagest can indeed be traced back to Hipparchus,[12] but not that the complete star catalogue was simply "copied". Rather, Hipparchus' major errors are no longer present in the Almagest[10] and, on the other hand, Hipparchus' star catalogue had some stars that are entirely absent from the Almagest.[10] It can be concluded that Hipparchus' star catalogue, while forming the basis, has been reobserved and revised.[10][11]
The figure he used is based on Hipparchus' own estimate for precession, which was 1° in 100 years, instead of the correct 1° in 72 years. Dating attempts through proper motion of the stars also appear to date the actual observation to Hipparchus' time instead of Ptolemy.[16]
Many of the longitudes and latitudes have been corrupted in the various manuscripts. Most of these errors can be explained by similarities in the symbols used for different numbers. For example, the Greek letters Α and Δ were used to mean 1 and 4 respectively, but because these look similar copyists sometimes wrote the wrong one. In Arabic manuscripts, there was confusion between for example 3 and 8 (ج and ح). (At least one translator also introduced errors. Gerard of Cremona, who translated an Arabic manuscript into Latin around 1175, put 300° for the latitude of several stars. He had apparently learned from Moors, who used the letter س (sin) for 300 (like the Hebrew ש (shin)), but the manuscript he was translating came from the East, where س was used for 60, like the Hebrew ס (samekh).)[17]
Even without the errors introduced by copyists, and even accounting for the fact that the longitudes are more appropriate for 58 AD than for 137 AD, the latitudes and longitudes are not fully accurate, with errors as great as large fractions of a degree. Some errors may be due to atmospheric refraction causing stars that are low in the sky to appear higher than where they really are.[18] A series of stars in Centaurus are off by a couple of degrees, including the star we call Alpha Centauri. These were probably measured by a different person or persons from the others, and in an inaccurate way.[19]
The star catalogue contains 48 constellations, which have different surface areas and numbers of stars. In Book VIII, Chapter 3, Ptolemy writes that the constellations should be outlined on a globe, but it is unclear exactly how he means this: should surrounding polygons be drawn or should the figures be sketched or even line figures be drawn? This is not stated.
Although no line figures have survived from antiquity, the figures can be reconstructed on the basis of the descriptions in the star catalogue: The exact celestial coordinates of the figures' heads, feet, arms, wings and other body parts are recorded.[10] It is therefore possible to draw the stick figures in the modern sense so that they fit the description in the Almagest.[note 3]
These constellations form the basis for the modern constellations that were formally adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1922, with official boundaries that were agreed in 1928.
Of the stars in the catalogue, 108 (just over 10%) were classified by Ptolemy as 'unformed', by which he meant lying outside the recognized constellation figures. These were later absorbed into their surrounding constellations or in some cases used to form new constellations.[20]
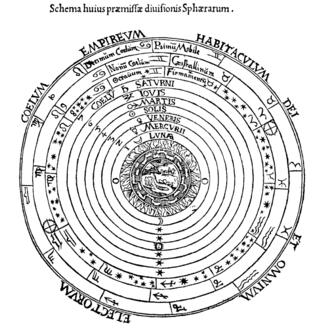
Ptolemy assigned the following order to the planetary spheres, beginning with the innermost:
Other classical writers suggested different sequences. Plato (c. 427 – c. 347 BC) placed the Sun second in order after the Moon. Martianus Capella (5th century AD) put Mercury and Venus in motion around the Sun. Ptolemy's authority was preferred by most medieval Islamic and late medieval European astronomers.
Ptolemy inherited from his Greek predecessors a geometrical toolbox and a partial set of models for predicting where the planets would appear in the sky. Apollonius of Perga (c. 262 – c. 190 BC) had introduced the deferent and epicycle and the eccentric deferent to astronomy. Hipparchus (2nd century BC) had crafted mathematical models of the motion of the Sun and Moon. Hipparchus had some knowledge of Mesopotamian astronomy, and he felt that Greek models should match those of the Babylonians in accuracy. He was unable to create accurate models for the remaining five planets.

The Syntaxis adopted Hipparchus' solar model, which consisted of a simple eccentric deferent. For the Moon, Ptolemy began with Hipparchus' epicycle-on-deferent, then added a device that historians of astronomy refer to as a "crank mechanism":[21] he succeeded in creating models for the other planets, where Hipparchus had failed, by introducing a third device called the equant.
Ptolemy wrote the Syntaxis as a textbook of mathematical astronomy. It explained geometrical models of the planets based on combinations of circles, which could be used to predict the motions of celestial objects. In a later book, the Planetary Hypotheses, Ptolemy explained how to transform his geometrical models into three-dimensional spheres or partial spheres. In contrast to the mathematical Syntaxis, the Planetary Hypotheses is sometimes described as a book of cosmology.


Ptolemy's comprehensive treatise of mathematical astronomy superseded most older texts of Greek astronomy. Some were more specialized and thus of less interest; others simply became outdated by the newer models. As a result, the older texts ceased to be copied and were gradually lost. Much of what we know about the work of astronomers like Hipparchus comes from references in the Syntaxis.
The first translations into Arabic were made in the 9th century, with two separate efforts, one sponsored by the caliph Al-Ma'mun, who received a copy as a condition of peace with the Byzantine emperor.[22] Sahl ibn Bishr is thought to be the first Arabic translator.
No Latin translation was made before the 12th century. Henry Aristippus made the first Latin translation directly from a Greek copy, but it was not as influential as a later translation into Latin made in Spain by the Italian scholar Gerard of Cremona from the Arabic (finished in 1175).[23][24] Gerard translated the Arabic text while working at the Toledo School of Translators, although he was unable to translate many technical terms such as the Arabic Abrachir for Hipparchus. In the 13th century a Spanish version was produced, which was later translated under the patronage of Alfonso X.
In the 15th century, a Greek version appeared in Western Europe. The German astronomer Johannes Müller (known as Regiomontanus, after his birthplace of Königsberg) made an abridged Latin version at the instigation of the Greek churchman Cardinal Bessarion. Around the same time, George of Trebizond made a full translation accompanied by a commentary that was as long as the original text. George's translation, done under the patronage of Pope Nicholas V, was intended to supplant the old translation. The new translation was a great improvement; the new commentary was not, and aroused criticism.[25] The Pope declined the dedication of George's work,[25] and Regiomontanus's translation had the upper hand for over 100 years.[citation needed]
During the 16th century, Guillaume Postel, who had been on an embassy to the Ottoman Empire, brought back Arabic disputations of the Almagest, such as the works of al-Kharaqī, Muntahā al-idrāk fī taqāsīm al-aflāk ("The Ultimate Grasp of the Divisions of Spheres", 1138–39).[26]
Commentaries on the Syntaxis were written by Theon of Alexandria (extant), Pappus of Alexandria (only fragments survive), and Ammonius Hermiae (lost).
Under the scrutiny of modern scholarship, and the cross-checking of observations contained in the Almagest against figures produced through backwards extrapolation, various patterns of errors have emerged within the work.[27][28] A prominent example is Ptolemy's use of measurements said to have been taken at noon, but which systematically produce readings that are off by half an hour, as if the observations were taken at 12:30pm.[27] However, an explanation for this error was found in 1969.[29][30][31]
The overall quality of Claudius Ptolemy's scholarship and place as "one of the most outstanding scientists of antiquity" has been challenged by several modern writers, most prominently by Robert R. Newton in the 1977 book The Crime of Claudius Ptolemy, which asserted that the scholar fabricated his observations to fit his theories. Newton accused Ptolemy of systematically inventing data or doctoring the data of earlier astronomers, and labelled him "the most successful fraud in the history of science".[27] One striking error noted by Newton was an autumn equinox said to have been observed by Ptolemy and "measured with the greatest care" at 2pm on 25 September 132, when the equinox should have been observed at 9:54am the day prior.[27] Herbert Lewis, who had reworked some of Ptolemy's calculations, agreed with Newton that "Ptolemy was an outrageous fraud", and that "all those results capable of statistical analysis point beyond question towards fraud and against accidental error".[28]
Although some have described the charges laid by Newton as "erudite and imposing", others have disagreed with the findings.[27] Bernard R. Goldstein wrote, "Unfortunately, Newton’s arguments in support of these charges are marred by all manner of distortions, misunderstandings, and excesses of rhetoric due to an intensely polemical style."[29] Owen Gingerich, while agreeing that the Almagest contains "some remarkably fishy numbers",[27] including in the matter of the 30-hour displaced equinox, which he noted aligned perfectly with predictions made by Hipparchus 278 years earlier,[32] rejected the qualification of fraud.[27][33] John Phillips Britton, Visiting Fellow at Yale University, wrote of R.R. Newton, "I think that his main conclusion with respect to Ptolemy’s stature and achievements as an astronomer is simply wrong, and that the Almagest should be seen as a great, if not indeed the first, scientific treatise." He continued, "Newton’s work does focus critical attention on the many difficulties and inconsistencies apparent in the fine structure of the Almagest. In particular, his conclusion that the Almagest is not a historical account of how Ptolemy actually derived his models and parameters is essentially the same as mine, although our reasons for this conclusion and our inferences from it differ radically."[31]
The Almagest under the Latin title Syntaxis mathematica, was edited by J. L. Heiberg in Claudii Ptolemaei opera quae exstant omnia, vols. 1.1 and 1.2 (1898, 1903).

Three translations of the Almagest into English have been published. The first, by R. Catesby Taliaferro of St. John's College in Annapolis, Maryland, was included in volume 16 of the Great Books of the Western World in 1952. The second, by G. J. Toomer, Ptolemy's Almagest in 1984, with a second edition in 1998.[34] The third was a partial translation by Bruce M. Perry in The Almagest: Introduction to the Mathematics of the Heavens in 2014.[35]
A direct French translation from the Greek text was published in two volumes in 1813 and 1816 by Nicholas Halma, including detailed historical comments in a 69-page preface. It has been described as "suffer[ing] from excessive literalness, particularly where the text is difficult" by Toomer, and as "very faulty" by Serge Jodra.[36] The scanned books are available in full at the Gallica French National library.[37][38]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.