a realtime plotting utility for text mode consoles and terminals with data input from stdin / pipe
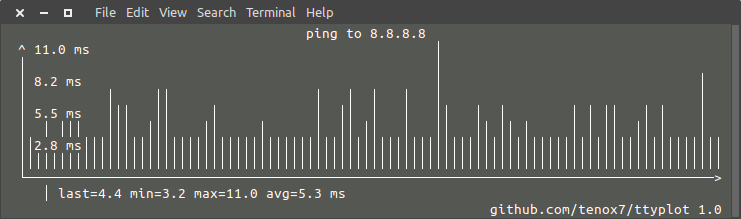
takes data from standard input / unix pipeline, most commonly some tool like ping, snmpget, netstat, ip link, ifconfig, sar, vmstat, etc. and plots in text mode on a terminal in real time, for example a simple ping:
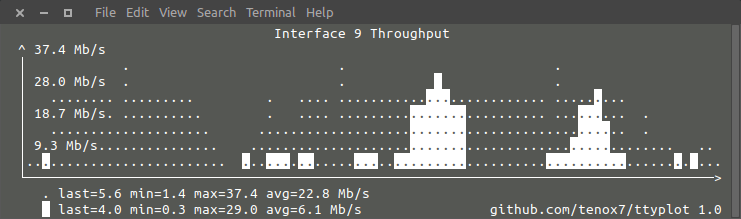
supports rate calculation for counters and up to two graphs on a single display using reverse video for second line, for example snmpget, ip link, rrdtool, etc:
snap install ttyplot
apt install ttyplot
alternatively download | tracker
emerge -av app-admin/ttyplot
brew install ttyplot
pkg install ttyplot
pkg install ttyplot
for other platforms see releases tab, also older versions
fflush() is needed to disable stdio buffering
vmstat -n 1 | gawk '{ print 100-int($(NF-2)); fflush(); }' | ttyplot -s 100 -t "CPU Usage" -u "%"
stdbuf is used to disable stdio buffering throughout the pipeline
free -m -s 1 | stdbuf -o0 grep "^Mem:" | stdbuf -o0 tr -s " " | stdbuf -o0 cut -d" " -f3 | ttyplot -t "MEM Usage" -u "MB"
vm_stat 1 | awk '{ print int($2)*4096/1024^3; fflush(); }' | ttyplot -t "MacOS Memory Usage" -u GB
vmstat -n 1 | perl -lane 'BEGIN{$|=1} print "@F[0,1]"' | ttyplot -2 -t "procs in R and D state"
{ while true; do uptime | gawk '{ gsub(/,/, ""); print $(NF-2) }'; sleep 1; done } | ttyplot -t "load average" -s load
on macOS change -u to -l
ping 8.8.8.8 | sed -u 's/^.*time=//g; s/ ms//g' | ttyplot -t "ping to 8.8.8.8" -u ms
{ while true; do iwconfig 2>/dev/null | grep "Signal level" | sed -u 's/^.*Signal level=-//g; s/dBm//g'; sleep 1; done } | ttyplot -t "wifi signal" -u "-dBm" -s 90
{ while true; do /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/Current/Resources/airport --getinfo | awk '/agrCtlRSSI/ {print -$2; fflush();}'; sleep 1; done } | ttyplot -t "wifi signal" -u "-dBm" -s 90
{ while true; do awk '{ printf("%.1f\n", $1/1000) }' /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp; sleep 1; done } | ttyplot -t "cpu temp" -u C
{ while true; do sensors | grep fan1: | tr -s " " | cut -d" " -f2; sleep 1; done } | ttyplot -t "fan speed" -u RPM
{ while true; do rrdtool lastupdate /var/lib/collectd/rrd/$(hostname)/memory/memory-used.rrd | awk 'END { print ($NF)/1024/1024 }'; sleep 1; done } | ttyplot -m $(awk '/MemTotal/ { print ($2)/1024 }' /proc/meminfo) -t "Memoru Used" -u MB
{ while true; do curl -sL https://api.coindesk.com/v1/bpi/currentprice.json | jq .bpi.USD.rate_float; sleep 600; done } | ttyplot -t "bitcoin price" -u usd
{ while true; do curl -sL https://api.iextrading.com/1.0/stock/googl/price; echo; sleep 600; done } | ttyplot -t "google stock price" -u usd
{ while true; do curl -s http://10.4.7.180:9100/metrics | grep "^node_load1 " | cut -d" " -f2; sleep 1; done } | ttyplot
ttyplot supports "two line" plot for in/out or read/write
snmpdelta -v 2c -c public -Cp 10 10.23.73.254 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.{10,16}.9 | gawk '{ print $NF/1000/1000/10; fflush(); }' | ttyplot -2 -t "interface 9 throughput" -u Mb/s
netstat -b -w ${1} -I em0 | awk 'NR>3 { print $1/1024; print $2/1024; fflush }' | ttyplot -2 -t "IN/OUT Bandwidth in KB/s (${1}s resolution)" -u "KB/s" -c "#"
sar -n DEV 1 | gawk '{ if($6 ~ /rxkB/) { print iin/1000; print out/1000; iin=0; out=0; fflush(); } iin=iin+$6; out=out+$7; }' | ttyplot -2 -u "MB/s"
iostat -xmy 1 nvme0n1 | stdbuf -o0 tr -s " " | stdbuf -o0 cut -d " " -f 4,5 | ttyplot -2 -t "nvme0n1 throughput" -u MB/s
ttyplot also supports counter style metrics, calculating rate by measured time difference between samples
{ while true; do snmpget -v 2c -c public 10.23.73.254 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.{10,16}.9 | awk '{ print $NF/1000/1000; }'; sleep 10; done } | ttyplot -2 -r -u "MB/s"
{ while true; do ip -s -j link show enp0s31f6 | jq .[].stats64.rx.bytes/1024/1024,.[].stats64.tx.bytes/1024/1024; sleep 1; done } | ttyplot -r -2 -u "MB/s"
{ while true; do curl -s http://10.11.0.173:9100/metrics | awk '/^node_disk_.+_bytes_total{device="sda"}/ { printf("%f\n", $2/1024/1024); }'; sleep 1; done } | ttyplot -r -2 -u MB/s -t "10.11.0.173 sda writes"
{ while true; do rrdtool lastupdate /var/lib/collectd/rrd/$(hostname)/interface-enp1s0/if_octets.rrd | awk 'END { print ($2)/1000/1000, ($3)/1000/1000 }'; sleep 10; done } | ttyplot -2 -r -t "enp1s0 throughput" -u MB/s
ttyplot [-2] [-r] [-c plotchar] [-s scale] [-m max] [-M min] [-t title] [-u unit]
ttyplot -h
ttyplot -v
-2 read two values and draw two plots, the second one is in reverse video
-r rate of a counter (divide value by measured sample interval)
-c character to use for plot line, eg @ # % . etc
-e character to use for error line when value exceeds hardmax (default: e)
-E character to use for error symbol displayed when value is less than hardmin (default: v)
-s initial scale of the plot (can go above if data input has larger value)
-m maximum value, if exceeded draws error line (see -e), upper-limit of plot scale is fixed
-M minimum value, if entered less than this, draws error symbol (see -E), lower-limit of the plot scale is fixed
-t title of the plot
-u unit displayed beside vertical bar
-v print the current version and exit
-h print this help message and exit
when reading data from a pipe, ttyplot accepts the following commands typed at the terminal:
q quit
r toggle rate mode
these commands do not work if the standard input is a terminal: in this case quit with Ctrl-C.
UPDATE as of version 1.5 ttyplot will print "input stream closed" and wait forever, instead of quititing.
this is by design; your problem is likely that the output is lost (terminal erased) when ttyplot exits; this is explained in the next question below
you can also simply work around it, by adding sleep, read, cat at the end of the stream:
{ echo 1 2 3; cat; } | ttyplot
this is because of alternate screen in terminals based on xterm; if you use one of these this will likely work around it:
echo 1 2 3 | TERM=vt100 ttyplot
you can also permanently fix terminfo entry (this will make a copy in $HOME/.terminfo/):
infocmp -I $TERM | sed -e 's/smcup=[^,]*,//g' -e 's/rmcup=[^,]*,//g' | tic -
press ctrl^j to re-set
by default in unix stdio is buffered, you can work around it in various ways also this
License: Apache 2.0
Copyright (c) 2013-2018 Antoni Sawicki
Copyright (c) 2019-2024 Google LLC
Copyright (c) 2023 Edgar Bonet
Copyright (c) 2023 Sebastian Pipping