|
|

William Cecil, after Marcus Gheeraerts.
National Portrait Gallery, London.
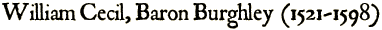
WILLIAM CECIL, LORD BURGHLEY (or Burleigh) was born, according to his own statement, on the 13th of September 1521 at the house
of his mother's father at Bourne, Lincolnshire. Pedigrees, elaborated by Cecil himself with the help of Camden,
the antiquary, associated him with the Cecils or Sitsyllts of Altyrennes in Herefordshire, and traced his descent from an Owen of the
time of King Harold and a Sitsyllt of the reign of Rufus. The connexion with the Herefordshire family is not so impossible as the descent
from Sitsyllt; but the earliest authentic ancestor of the lord treasurer is his grandfather, David, who, according to Burghley's enemies,
"kept the best inn" in Stamford. David somehow secured the favour of Henry VII, to whom he seems to have been
yeoman of the guard. He was serjeant-at-arms to Henry VIII in 1526, sheriff
of Northamptonshire in 1532, and a justice of the peace for Rutland. His eldest son, Richard, yeoman of the wardrobe (d. 1554), married
Jane, daughter of William Heckington of Bourne, and was father of three daughters and Lord Burghley.
William, the only son, was put to school first at Grantham and then at Stamford. In May 1535, at the age of fourteen, he went up to St
John's College, Cambridge, where he was brought into contact with the foremost educationists of the time,
Roger Ascham and John Cheke, and acquired an unusual
knowledge of Greek. He also acquired the affections of Cheke's sister, Mary, and was in 1541 removed by his father to Gray's Inn,
without, after six years' residence at Cambridge, having taken a degree. The precaution proved useless, and four months later Cecil
committed one of the rare rash acts of his life in marrying Mary Cheke. The only child of this marriage, Thomas, the future earl of
Exeter, was born in May 1542, and in February 1543 Cecil's first wife died. Three years later he married (21st of December 1546) Mildred,
daughter of Sir Anthony Cooke, who was ranked by Ascham with Lady Jane Grey as one of the two most learned
ladies in the kingdom, and whose sister, Anne, became the wife of Sir Nicholas Bacon and the mother of
Sir Francis Bacon.
Cecil, meanwhile, had obtained the reversion to the office of custos rotulorum brevium, and, according to his autobiographical
notes, sat in parliament in 1543; but his name does not occur in the imperfect parliamentary returns until 1547, when he was elected
for the family borough of Stamford. Earlier in that year he had accompanied Protector Somerset on his
Pinkie campaign, being one of the two "judges of the Marshalsea," i.e. in the courts-martial. The other was William Patten, who states
that both he and Cecil began to write independent accounts of the campaign, and that Cecil generously communicated his notes for Patten's
narrative, which has been reprinted more than once.
In 1548 he is described as the protector's master of requests, which apparently means that he was clerk or registrar of the court of
requests which the protector, possibly at Latimer's instigation, illegally
set up in Somerset House "to hear poor men's complaints." He also seems to have acted as private secretary to the protector, and was
in some danger at the time of the protector's fall (October 1549). The lords opposed to Somerset ordered his detention on the l0th of
October, and in November he was in the Tower. On the 25th of January 1550 he was bound over in recognizances to the value of a thousand
marks. However, he soon ingratiated himself with Warwick, and on the 15th of September 1550 he was
sworn one of the king's two secretaries. He was knighted on the 11th of October 1551, on the eve of
Somerset's second fall, and was congratulated on his success in escaping his benefactor's fate.
In April he became chancellor of the order of the Garter. But service under Northumberland was no bed
of roses, and in his diary Cecil recorded his release in the phrase ex misero aulico factus liber et meijuris. His responsibility
for Edward's illegal "devise" of the crown [i.e., in favor of
Lady Jane Grey] has been studiously minimized by Cecil himself and by his biographers. Years afterwards,
he pretended that he had only signed the "devise" as a witness, but in his apology to Queen Mary he did not
venture to allege so flimsy an excuse; he preferred to lay stress on the extent to which he succeeded in shifting the responsibility on
to the shoulders of his brother-in-law, Sir John Cheke, and other friends, and on his intrigues to frustrate the queen to whom he had
sworn allegiance. There is no doubt that he saw which way the wind was blowing, and disliked Northumberland's scheme; but he had not the
courage to resist the duke to his face. As soon, however, as the duke had set out to meet Mary, Cecil became the most active intriguer
against him, and to these efforts, of which he laid a full account before Queen Mary, he mainly owed his immunity. He had, moreover, had
no part in the divorce of Catherine or in the humiliation of Mary in Henry's
reign, and he made no scruple about conforming to the religious reaction. He went to mass, confessed, and out of sheer zeal and in no
official capacity went to meet Cardinal Pole on his pious mission
to England in December 1554, again accompanying him to Calais in May 1555.
It was rumoured in December 1554 that Cecil would succeed Sir William Petre as secretary, an office which, with
his chancellorship of the Garter, he had lost on Mary's accession. Probably the queen had more to do with the falsification of this rumour
than Cecil, though he is said to have opposed in the parliament of 1555 — in which he represented Lincolnshire — a bill for
the confiscation of the estates of the Protestant refugees. But the story, even as told by his biographer (Peck, Desiderata Curiosa,
1) does not represent Cecil's conduct as having been very courageous; and it is more to his credit that he found no seat in the parliament
of 1558, for which Mary had directed the return of "discreet and good Catholic members." By that time Cecil had begun to trim his sails to
a different breeze.
He was in secret communication with Elizabeth before Mary died, and from the first
the new queen relied on Cecil as she relied on no one else. Her confidence was not misplaced; Cecil was exactly the kind of minister England
then required. Personal experience had ripened his rare natural gift for avoiding dangers. It was no time for brilliant initiative or
adventurous politics; the need was to avoid Scylla and Charybdis, and a via media had to be found in church and state, at home and
abroad. Cecil was not a political genius; no great ideas emanated from his brain. But he was eminently a safe man, not an original thinker,
but a counsellor of unrivalled wisdom. Caution was his supreme characteristic; he saw that above all things England required time. Like
Fabius, he restored the fortunes of his country by deliberation. He averted open rupture until England was strong enough to stand the shock.
There was nothing heroic about Cecil or his policy; it involved a callous attitude towards struggling Protestants abroad. Huguenots and Dutch
were aided just enough to keep them going in the struggles which warded danger off from England's shores. But Cecil never developed that
passionate aversion from decided measures which became a second nature to his mistress. His intervention in Scotland in 1559-1560 showed that
he could strike on occasion; and his action over the execution of Mary, Queen of Scots, proved that he was
willing to take responsibility from which Elizabeth shrank. Generally he was in favour of more decided intervention on behalf of continental
Protestants than Elizabeth would admit; but it is not always easy to ascertain the advice he gave.
He has left endless memoranda lucidly setting forth the pros and cons of every course of action; but there are few indications of the line
which he actually recommended when it came to a decision. How far he was personally responsible for the Anglican Settlement, the Poor Laws,
and the foreign policy of the reign, how far he was thwarted by the baleful influence of Leicester and the caprices
of the queen, remains to a large extent a matter of conjecture. His share in the settlement of 1559 was considerable, and it coincided fairly
with his own somewhat indeterminate religious views. Like the mass of the nation, he grew more Protestant as time wore on; he was readier to
persecute Papists than Puritans; he had no love for ecclesiastical jurisdiction, and he warmly remonstrated with Whitgift
over his persecuting Articles of 1583 [see Letter to Whitgift, 1584].
The finest encomium was passed on him by the queen herself, when she said, "This judgment I have of you, that you will not be corrupted with
any manner of gifts, and that you will be faithful to the state."
From 1558 for forty years the biography of Cecil is almost indistinguishable from that of Elizabeth and from the history of England. Of personal
incident, apart from his mission to Scotland in 1560, there is little. He represented Lincolnshire in the parliament of 1559, and Northamptonshire
in that of 1563, and he took an active part in the proceedings of the House of Commons until his elevation to the peerage; but there seems no good
evidence for the story that he was proposed as speaker in 1563. In January 1561 he was given the lucrative office of master of the court of wards
in succession to Sir Thomas Parry, and he did something to reform that instrument of tyranny and abuse. In February 1559 he was elected chancellor
of Cambridge University in succession to Cardinal Pole; he was created M.A. of that university on the occasion of
Elizabeth's visit in 1564, and M.A. of Oxford on a similar occasion in 1566.
On the 25th of February 1571 he was raised to the peerage as Baron Burghley of Burghley (or Burleigh); the fact that he continued to act as
secretary after his elevation illustrates the growing importance of that office, which under his son became a secretaryship of state. In 1572,
however, the marquess of Winchester, who had been lord high treasurer under
Edward, Mary and Elizabeth, died, and Burghley succeeded to his post. It was a signal triumph over Leicester; and,
although Burghley had still to reckon with cabals in the council and at court, his hold over the queen strengthened with the lapse of years. Before
he died, Robert, his only surviving son by his second wife, was ready to step into his shoes as the queen's principal adviser.
Having survived all his rivals, and all his children except Robert and the worthless Thomas, Burghley died at his London house on the 4th of August
1598, and was buried in St Martin's, Stamford.
 Burghley's private life was singularly virtuous; he was a faithful husband, a careful father and a considerate master. A book-lover and antiquary, he made a special hobby of heraldry and genealogy. It was the conscious and unconscious aim of the age to reconstruct a new landed aristocracy on the ruins of the old, and Burghley was a great builder and planter. All the arts of architecture and horticulture were lavished on Burghley House and Theobalds, which his son exchanged for Hatfield. His public conduct does not present itself in quite so amiable a light. As the marquess of Winchester said of himself, he was sprung from the willow rather than the oak, and he was not the man to suffer for convictions. The interest of the state was the supreme consideration, and to it he had no hesitation in sacrificing individual consciences. Burghley's private life was singularly virtuous; he was a faithful husband, a careful father and a considerate master. A book-lover and antiquary, he made a special hobby of heraldry and genealogy. It was the conscious and unconscious aim of the age to reconstruct a new landed aristocracy on the ruins of the old, and Burghley was a great builder and planter. All the arts of architecture and horticulture were lavished on Burghley House and Theobalds, which his son exchanged for Hatfield. His public conduct does not present itself in quite so amiable a light. As the marquess of Winchester said of himself, he was sprung from the willow rather than the oak, and he was not the man to suffer for convictions. The interest of the state was the supreme consideration, and to it he had no hesitation in sacrificing individual consciences.
He frankly disbelieved in toleration; "that state," he said, "could never be in safety where there was a toleration of two religions. For there is
no enmity so great as that for religion; and therefore they that differ in the service of their God can never agree in the service of their country."
With a maxim such as this, it was easy for him to maintain that Elizabeth's coercive measures were political and not religious. To say that he was
Machiavellian is meaningless, for every statesman is so more or less; especially in the 16th century men preferred efficiency to principle. On the
other hand, principles are valueless without law and order; and Burghley's craft and subtlety prepared a security in which principles might find
some scope.
Excerpted from:
Encyclopedia Britannica, 11th Ed. Vol IV.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1910. 817.
Other Local Resources:
Books for further study:
Alford, Stephen. Burghley: William Cecil at the Court of Elizabeth I
New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 2011.
Alford, Stephen. The Early Elizabethan Polity: William Cecil and
the British Succession Crisis, 1558-1569.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002.
Alford, Stephen. The Watchers: A Secret History of the Reign of Elizabeth I
London: Bloomsbury Press, 2012.
Croft, Pauline. Patronage, Culture and Power: The Early Cecils.
Paul Mellon Center, 2004.
Graves, Michael. Burghley: William Cecil, Lord Burghley.
Addison Wesley Publishing Company, 1998.
Loades, David. The Cecils: Privilege and Power Behind the Throne.
London: Bloomsbury Academic, 2009.
Smith, Alan Gordon. William Cecil: The Power Behind Elizabeth.
University Press of the Pacific, 2004.
William Cecil on the Web:
 | to Henry VIII |
 | to Elizabeth I |
 | to Renaissance English Literature |
 | to Luminarium Encyclopedia |
|
Index of Encyclopedia Entries:
Medieval Cosmology
Prices of Items in Medieval England
Edward II
Isabella of France, Queen of England
Piers Gaveston
Thomas of Brotherton, E. of Norfolk
Edmund of Woodstock, E. of Kent
Thomas, Earl of Lancaster
Henry of Lancaster, Earl of Lancaster
Henry of Grosmont, Duke of Lancaster
Roger Mortimer, Earl of March
Hugh le Despenser the Younger
Bartholomew, Lord Burghersh, elder
Hundred Years' War (1337-1453)
Edward III
Philippa of Hainault, Queen of England
Edward, Black Prince of Wales
John of Eltham, Earl of Cornwall
The Battle of Crécy, 1346
The Siege of Calais, 1346-7
The Battle of Poitiers, 1356
Lionel of Antwerp, Duke of Clarence
John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster
Edmund of Langley, Duke of York
Thomas of Woodstock, Gloucester
Richard of York, E. of Cambridge
Richard Fitzalan, 3. Earl of Arundel
Roger Mortimer, 2nd Earl of March
The Good Parliament, 1376
Richard II
The Peasants' Revolt, 1381
Lords Appellant, 1388
Richard Fitzalan, 4. Earl of Arundel
Archbishop Thomas Arundel
Thomas de Beauchamp, E. Warwick
Robert de Vere, Earl of Oxford
Ralph Neville, E. of Westmorland
Thomas Mowbray, Duke of Norfolk
Edmund Mortimer, 3. Earl of March
Roger Mortimer, 4. Earl of March
John Holland, Duke of Exeter
Michael de la Pole, E. Suffolk
Hugh de Stafford, 2. E. Stafford
Henry IV
Edward, Duke of York
Edmund Mortimer, 5. Earl of March
Henry Percy, Earl of Northumberland
Sir Henry Percy, "Harry Hotspur"
Thomas Percy, Earl of Worcester
Owen Glendower
The Battle of Shrewsbury, 1403
Archbishop Richard Scrope
Thomas Mowbray, 3. E. Nottingham
John Mowbray, 2. Duke of Norfolk
Thomas Fitzalan, 5. Earl of Arundel
Henry V
Thomas, Duke of Clarence
John, Duke of Bedford
Humphrey, Duke of Gloucester
John Talbot, Earl of Shrewsbury
Richard, Earl of Cambridge
Henry, Baron Scrope of Masham
William de la Pole, Duke of Suffolk
Thomas Montacute, E. Salisbury
Richard Beauchamp, E. of Warwick
Henry Beauchamp, Duke of Warwick
Thomas Beaufort, Duke of Exeter
Cardinal Henry Beaufort
John Beaufort, Earl of Somerset
Sir John Fastolf
John Holland, 2. Duke of Exeter
Archbishop John Stafford
Archbishop John Kemp
Catherine of Valois
Owen Tudor
John Fitzalan, 7. Earl of Arundel
John, Lord Tiptoft
Charles VII, King of France
Joan of Arc
Louis XI, King of France
Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy
The Battle of Agincourt, 1415
The Battle of Castillon, 1453
The Wars of the Roses 1455-1485
Causes of the Wars of the Roses
The House of Lancaster
The House of York
The House of Beaufort
The House of Neville
The First Battle of St. Albans, 1455
The Battle of Blore Heath, 1459
The Rout of Ludford, 1459
The Battle of Northampton, 1460
The Battle of Wakefield, 1460
The Battle of Mortimer's Cross, 1461
The 2nd Battle of St. Albans, 1461
The Battle of Towton, 1461
The Battle of Hedgeley Moor, 1464
The Battle of Hexham, 1464
The Battle of Edgecote, 1469
The Battle of Losecoat Field, 1470
The Battle of Barnet, 1471
The Battle of Tewkesbury, 1471
The Treaty of Pecquigny, 1475
The Battle of Bosworth Field, 1485
The Battle of Stoke Field, 1487
Henry VI
Margaret of Anjou
Richard Plantagenet, Duke of York
Edward IV
Elizabeth Woodville
Richard Woodville, 1. Earl Rivers
Anthony Woodville, 2. Earl Rivers
Jane Shore
Edward V
Richard III
George, Duke of Clarence
Ralph Neville, 2. Earl of Westmorland
Richard Neville, Earl of Salisbury
Richard Neville, Earl of Warwick
Edward Neville, Baron Bergavenny
William Neville, Lord Fauconberg
Robert Neville, Bishop of Salisbury
John Neville, Marquis of Montagu
George Neville, Archbishop of York
John Beaufort, 1. Duke Somerset
Edmund Beaufort, 2. Duke Somerset
Henry Beaufort, 3. Duke of Somerset
Edmund Beaufort, 4. Duke Somerset
Margaret Beaufort
Edmund Tudor, Earl of Richmond
Jasper Tudor, Earl of Pembroke
Humphrey Stafford, D. Buckingham
Henry Stafford, Duke of Buckingham
Humphrey Stafford, E. of Devon
Thomas, Lord Stanley, Earl of Derby
Sir William Stanley
Archbishop Thomas Bourchier
Henry Bourchier, Earl of Essex
John Mowbray, 3. Duke of Norfolk
John Mowbray, 4. Duke of Norfolk
John Howard, Duke of Norfolk
Henry Percy, 2. E. Northumberland
Henry Percy, 3. E. Northumberland
Henry Percy, 4. E. Northumberland
William, Lord Hastings
Henry Holland, Duke of Exeter
William Fitzalan, Earl of Arundel
William Herbert, 1. Earl of Pembroke
John de Vere, 12th Earl of Oxford
John de Vere, 13th Earl of Oxford
Thomas de Clifford, 8. Baron Clifford
John de Clifford, 9. Baron Clifford
John Tiptoft, Earl of Worcester
Thomas Grey, 1. Marquis Dorset
Sir Andrew Trollop
Archbishop John Morton
Edward Plantagenet, E. of Warwick
John Talbot, 2. E. Shrewsbury
John Talbot, 3. E. Shrewsbury
John de la Pole, 2. Duke of Suffolk
John de la Pole, E. of Lincoln
Edmund de la Pole, E. of Suffolk
Richard de la Pole
John Sutton, Baron Dudley
James Butler, 5. Earl of Ormonde
Sir James Tyrell
Edmund Grey, first Earl of Kent
George Grey, 2nd Earl of Kent
John, 5th Baron Scrope of Bolton
James Touchet, 7th Baron Audley
Walter Blount, Lord Mountjoy
Robert Hungerford, Lord Moleyns
Thomas, Lord Scales
John, Lord Lovel and Holand
Francis Lovell, Viscount Lovell
Sir Richard Ratcliffe
William Catesby
Ralph, 4th Lord Cromwell
Jack Cade's Rebellion, 1450
Tudor Period
King Henry VII
Queen Elizabeth of York
Arthur, Prince of Wales
Lambert Simnel
Perkin Warbeck
The Battle of Blackheath, 1497
King Ferdinand II of Aragon
Queen Isabella of Castile
Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
King Henry VIII
Queen Catherine of Aragon
Queen Anne Boleyn
Queen Jane Seymour
Queen Anne of Cleves
Queen Catherine Howard
Queen Katherine Parr
King Edward VI
Queen Mary I
Queen Elizabeth I
Henry Fitzroy, Duke of Richmond
Margaret Tudor, Queen of Scotland
James IV, King of Scotland
The Battle of Flodden Field, 1513
James V, King of Scotland
Mary of Guise, Queen of Scotland
Mary Tudor, Queen of France
Louis XII, King of France
Francis I, King of France
The Battle of the Spurs, 1513
Field of the Cloth of Gold, 1520
Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Eustace Chapuys, Imperial Ambassador
The Siege of Boulogne, 1544
Cardinal Thomas Wolsey
Archbishop Thomas Cranmer
Thomas Cromwell, Earl of Essex
Thomas, Lord Audley
Thomas Wriothesley, E. Southampton
Sir Richard Rich
Edward Stafford, D. of Buckingham
Thomas Howard, 2nd Duke of Norfolk
Thomas Howard, 3rd Duke of Norfolk
John Dudley, Duke of Northumberland
Charles Brandon, Duke of Suffolk
Thomas Boleyn, Earl of Wiltshire
George Boleyn, Viscount Rochford
John Russell, Earl of Bedford
Thomas Grey, 2. Marquis of Dorset
Henry Grey, D. of Suffolk
Charles Somerset, Earl of Worcester
George Talbot, 4. E. Shrewsbury
Francis Talbot, 5. E. Shrewsbury
Henry Algernon Percy,
5th Earl of Northumberland
Henry Algernon Percy,
6th Earl of Northumberland
Ralph Neville, 4. E. Westmorland
Henry Neville, 5. E. Westmorland
William Paulet, Marquis of Winchester
Sir Francis Bryan
Sir Nicholas Carew
John de Vere, 15th Earl of Oxford
John de Vere, 16th Earl of Oxford
Thomas Seymour, Lord Admiral
Edward Seymour, Protector Somerset
Margaret Pole, Countess of Salisbury
Henry Pole, Lord Montague
Sir Geoffrey Pole
Thomas Manners, Earl of Rutland
Henry Manners, Earl of Rutland
Henry Bourchier, 2. Earl of Essex
Robert Radcliffe, 1. Earl of Sussex
Henry Radcliffe, 2. Earl of Sussex
George Hastings, Earl of Huntingdon
Henry Courtenay, Marquis of Exeter
George Neville, Baron Bergavenny
Sir Edward Neville
William, Lord Paget
William Sandys, Baron Sandys
William Fitzwilliam, E. Southampton
Sir Anthony Browne
Sir Thomas Wriothesley
Sir William Kingston
George Brooke, Lord Cobham
Sir Richard Southwell
Thomas Fiennes, 9th Lord Dacre
Sir Francis Weston
Henry Norris
Lady Jane Grey
Sir Thomas Arundel
Sir Richard Sackville
Sir William Petre
Sir John Cheke
Walter Haddon, L.L.D
Sir Peter Carew
Sir John Mason
Nicholas Wotton
John Taylor
Sir Thomas Wyatt, the Younger
Cardinal Lorenzo Campeggio
Cardinal Reginald Pole
Stephen Gardiner, Bishop of Winchester
Edmund Bonner, Bishop of London
Nicholas Ridley, Bishop of London
John Hooper, Bishop of Gloucester
John Aylmer, Bishop of London
Thomas Linacre
William Grocyn
Archbishop William Warham
Cuthbert Tunstall, Bishop of Durham
Richard Fox, Bishop of Winchester
Edward Fox, Bishop of Hereford
Pope Julius II
Pope Leo X
Pope Clement VII
Pope Paul III
Pope Pius V
Pico della Mirandola
Desiderius Erasmus
Martin Bucer
Richard Pace
Christopher Saint-German
Thomas Tallis
Elizabeth Barton, the Nun of Kent
Hans Holbein, the Younger
The Sweating Sickness
Dissolution of the Monasteries
Pilgrimage of Grace, 1536
Robert Aske
Anne Askew
Lord Thomas Darcy
Sir Robert Constable
Oath of Supremacy
The Act of Supremacy, 1534
The First Act of Succession, 1534
The Third Act of Succession, 1544
The Ten Articles, 1536
The Six Articles, 1539
The Second Statute of Repeal, 1555
The Act of Supremacy, 1559
Articles Touching Preachers, 1583
Queen Elizabeth I
William Cecil, Lord Burghley
Robert Cecil, 1st Earl of Salisbury
Sir Francis Walsingham
Sir Nicholas Bacon
Sir Thomas Bromley
Robert Dudley, Earl of Leicester
Ambrose Dudley, Earl of Warwick
Henry Carey, Lord Hunsdon
Sir Thomas Egerton, Viscount Brackley
Sir Francis Knollys
Katherine "Kat" Ashley
Lettice Knollys, Countess of Leicester
George Talbot, 6. E. of Shrewsbury
Elizabeth, Countess of Shrewsbury
Gilbert Talbot, 7. E. of Shrewsbury
Sir Henry Sidney
Sir Robert Sidney
Archbishop Matthew Parker
Walter Devereux, 1st Earl of Essex
Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex
Penelope Devereux, Lady Rich
Sir Christopher Hatton
Edward Courtenay, E. Devonshire
Edward Manners, 3rd Earl of Rutland
Thomas Radcliffe, 3. Earl of Sussex
Henry Radcliffe, 4. Earl of Sussex
Robert Radcliffe, 5. Earl of Sussex
William Parr, Marquis of Northampton
Henry Wriothesley, 2. Southampton
Henry Wriothesley, 3. Southampton
Charles Neville, 6. E. Westmorland
Thomas Percy, 7. E. Northumberland
Henry Percy, 8. E. Northumberland
Henry Percy, 9. E. Nothumberland
William Herbert, 1. Earl of Pembroke
Charles, Lord Howard of Effingham
Thomas Howard, 4th Duke of Norfolk
Henry Howard, 1. Earl of Northampton
Thomas Howard, 1. Earl of Suffolk
Henry Hastings, 3. E. of Huntingdon
Edward Manners, 3rd Earl of Rutland
Roger Manners, 5th Earl of Rutland
Francis Manners, 6th Earl of Rutland
Henry FitzAlan, 12. Earl of Arundel
Thomas, Earl Arundell of Wardour
Edward Somerset, E. of Worcester
William Davison
Sir Walter Mildmay
Sir Ralph Sadler
Sir Amyas Paulet
Gilbert Gifford
Anthony Browne, Viscount Montague
François, Duke of Alençon & Anjou
Mary, Queen of Scots
Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley
James Hepburn, Earl of Bothwell
Anthony Babington and the Babington Plot
John Knox
Philip II of Spain
The Spanish Armada, 1588
Sir Francis Drake
Sir John Hawkins
William Camden
Archbishop Whitgift
Martin Marprelate Controversy
John Penry (Martin Marprelate)
Richard Bancroft, Archbishop of Canterbury
John Dee, Alchemist
Philip Henslowe
Edward Alleyn
The Blackfriars Theatre
The Fortune Theatre
The Rose Theatre
The Swan Theatre
Children's Companies
The Admiral's Men
The Lord Chamberlain's Men
Citizen Comedy
The Isle of Dogs, 1597
Common Law
Court of Common Pleas
Court of King's Bench
Court of Star Chamber
Council of the North
Fleet Prison
Assize
Attainder
First Fruits & Tenths
Livery and Maintenance
Oyer and terminer
Praemunire
The Stuarts
King James I of England
Anne of Denmark
Henry, Prince of Wales
The Gunpowder Plot, 1605
George Villiers, 1st Duke of Buckingham
Robert Carr, Earl of Somerset
Arabella Stuart, Lady Lennox
William Alabaster
Bishop Hall
Bishop Thomas Morton
Archbishop William Laud
John Selden
Lucy Harington, Countess of Bedford
Henry Lawes
King Charles I
Queen Henrietta Maria
Long Parliament
Rump Parliament
Kentish Petition, 1642
Thomas Wentworth, Earl of Strafford
John Digby, Earl of Bristol
George Digby, 2nd Earl of Bristol
Thomas Fairfax, 3rd Lord Fairfax
Robert Devereux, 3rd E. of Essex
Robert Sidney, 2. E. of Leicester
Algernon Percy, E. of Northumberland
Henry Montagu, Earl of Manchester
Edward Montagu, 2. Earl of Manchester
The Restoration
King Charles II
King James II
Test Acts
Greenwich Palace
Hatfield House
Richmond Palace
Windsor Palace
Woodstock Manor
The Cinque Ports
Mermaid Tavern
Malmsey Wine
Great Fire of London, 1666
Merchant Taylors' School
Westminster School
The Sanctuary at Westminster
"Sanctuary"
Images:
Chart of the English Succession from William I through Henry VII
Medieval English Drama
London c1480, MS Royal 16
London, 1510, the earliest view in print
Map of England from Saxton's Descriptio Angliae, 1579
London in late 16th century
Location Map of Elizabethan London
Plan of the Bankside, Southwark, in Shakespeare's time
Detail of Norden's Map of the Bankside, 1593
Bull and Bear Baiting Rings from the Agas Map (1569-1590, pub. 1631)
Sketch of the Swan Theatre, c. 1596
Westminster in the Seventeenth Century, by Hollar
Visscher's View of London, 1616
Larger Visscher's View in Sections
c. 1690. View of London Churches, after the Great Fire
The Yard of the Tabard Inn from Thornbury, Old and New London
|
|